- About Us
- One Stop Service
- Platform
In-Vitro
Molecular Assays
Cell-Based Functional Assays
In-Vivo
Pharmacology
Cancer PharmacologyInflammation Pharmacology - Join Us
- Contact Us

Research Techniques
AI approaches, which involves computationally analyzing vast virtual libraries of small molecules based on various traits like predicted specificity for specific drug targets in order to identify a small subset to test in lab experiments, has recently resulted in the entry of a number of drug candidates into clinical trials. There have been several examples of drug candidates with unique chemical structures for important targets or that target novel biology, which are typical early-stage research indicators of the influence of AI on small-molecule drug development. How successfully AI could deliver on its broader promise to boost clinical success rates and lower drug R&D costs will become obvious as the pool of these drug candidates expands and they go through the clinic in the coming years.
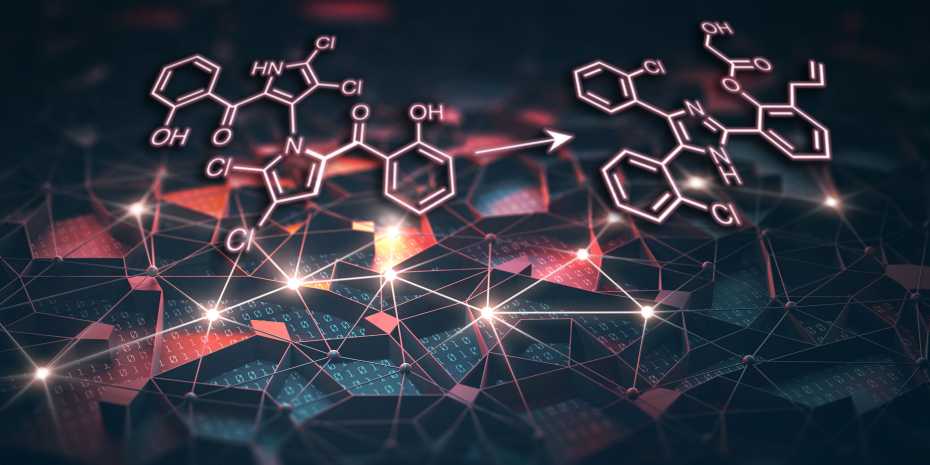
There have been several examples of drug candidates with unique chemical structures for important targets or that target novel biology, which are typical early-stage research indicators of the influence of AI on small-molecule drug development thus far. How successfully AI could deliver on its broader promise to boost clinical success rates and lower drug R&D costs will become obvious as the pool of these drug candidates expands and they go through the clinic in the coming years. Epigenetics, genomes, proteomics, metabolomics, and other fields fall under the purview of artificial intelligence analysis while looking for new anticancer targets. We must use artificial intelligence biology analysis to successfully integrate multiple omics data, address the complexity of cancer that results from interactions between genes and their products, and advance our understanding of carcinogenesis because it is not accurate to have anticancer targets by single omics studies. Therefore, an important future study area will be how to use AI biology analysis algorithms to combine multiomics data and find new anticancer targets.
.png)
References: doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d43747-022-00104-7, You, Y., Lai, X., Pan, Y. et al. Artificial intelligence in cancer target identification and drug discovery. Sig Transduct Target Ther 7, 156 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-022-00994-0

Shanghai Novopathway Biotechnology
Building No.5, East Huaxia Road No.333, Pudong New Area, Shanghai
BD Cooperation Email: BD@novopathway.com Tel: 021-5838 0618-501
Join Us Email: HR@novopathway.com Tel: 021-5838 0356

Beijing Sun-Novo Pharmaceutical Research
Building No.7, West Shuangying Road No.79 , Changping Area, Beijing
Website: http://www.sun-novo.com



