- About Us
- One Stop Service
- Platform
In-Vitro
Molecular Assays
Cell-Based Functional Assays
In-Vivo
Pharmacology
Cancer PharmacologyInflammation Pharmacology - Join Us
- Contact Us
- Drug Discovery
- Molecular Assays
- Cell-Based Functional Assays
- Immune Functional Assays
- Tumor Pharmacology Platform
- Inflammation Pharmacology Platform
- In-Vitro ADME/DMPK
- In-Vitro Toxicology
- Pharmacology
- Cancer Pharmacology
- Inflammation Pharmacology
- In-Vivo ADME/DMPK
- In-Vivo Toxicology
- In-Vivo Pathology
- Clinical Laboratory
PROteolysis Targeting Chimera (PROTAC) drugs
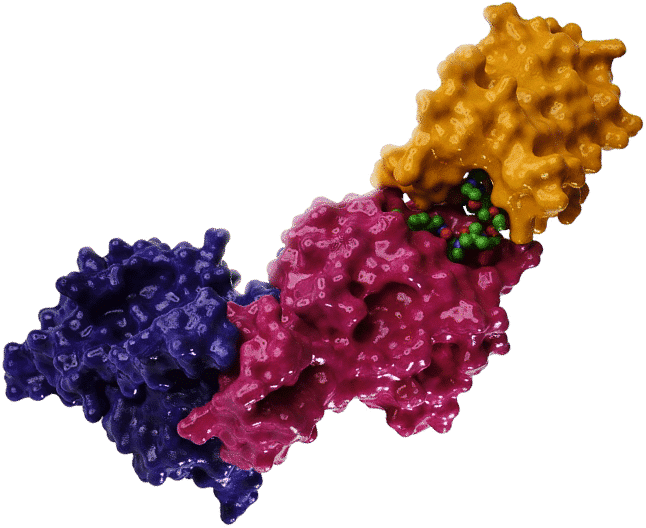
Heterobifunctional molecules that highjack ubiquitin ligase and targets cellular proteins for degradation.
Advantages:
Taking aim at the "Undruggable"
Multiple delivery methods
The ability to cross blood-brain barrier
Possibility of tissue-specific targeting
Benefits of tiny molecules
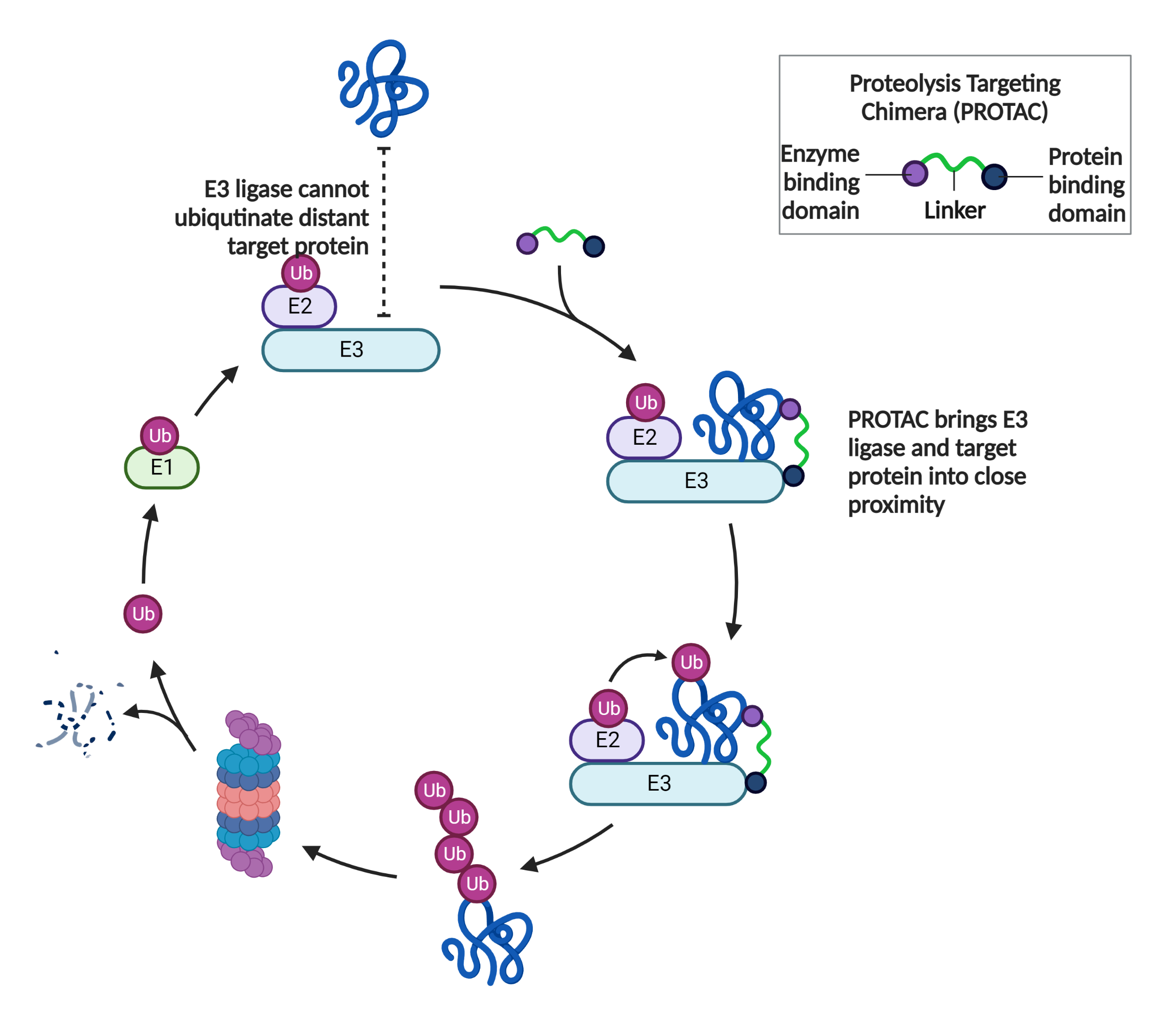
Why PROTAC?
What are the advantages of PROTAC over other molecular glue degraders?
.png)
PROTAC Discovery Workflow
_30sh.png)
_z3tj.png)
What are the challenges?
Membrane permeation mechanism
Temary crystal structures difficult to capture or identify
ADME & toxicity studies
What are the disadvantages?
Size-induced difficulties in clinic
Lengthy discovery phase
Off-target effect
Hook effect
PROTAC drug development:
Degradation efficacy: Time and degradation percentage.
Hook effect: Negatively impacts target degradation with excessive concentration of PROTAC.
Cooperativity: Favorable interactions between target protein and E3 ligase enable positive cooperativity
occurs when repulsive interactions inhibit the ternary complex formation.
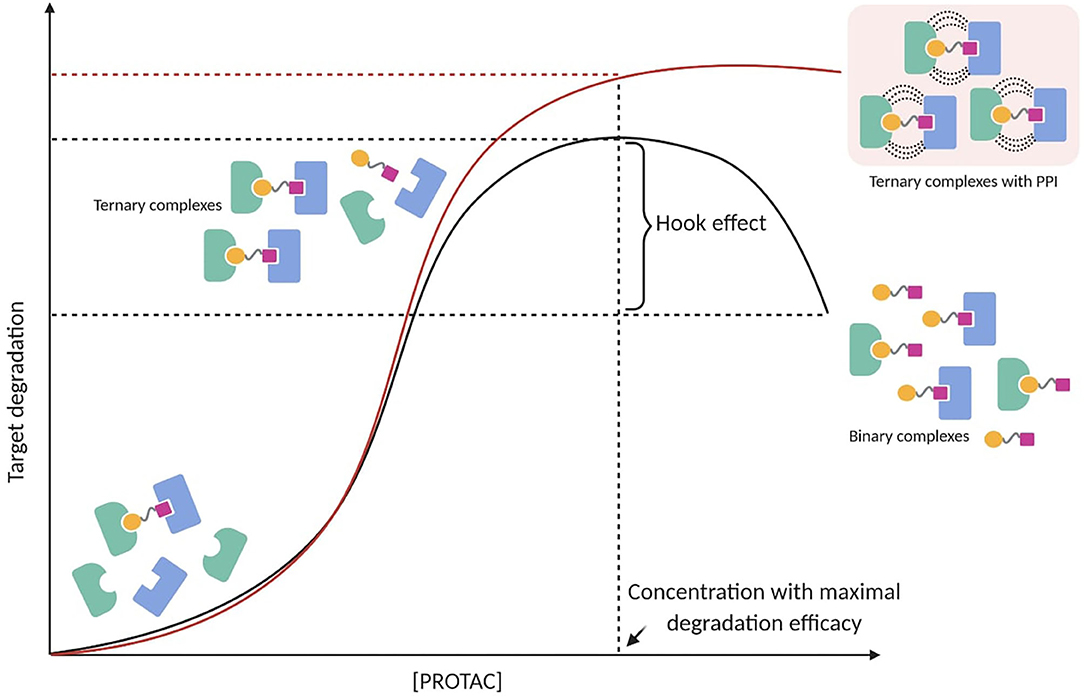
PROTAC-mediated ternary complex formation and hook effect. The hook effect is a function of PROTAC concentration (black line). A possible strategy to reduce the hook effect is increasing cooperative-binding PPIs to stabilize ternary complexes (red line).
Reference
Cecchini C, Pannilunghi S, Tardy S, Scapozza L. From Conception to Development: Investigating PROTACs Features for Improved Cell Permeability and Successful Protein Degradation. Front Chem. 2021;9:672267. Published 2021 Apr 20. doi:10.3389/fchem.2021.672267
For one-stop PROTAC service please click here.

Shanghai Novopathway Biotechnology
Building No.5, East Huaxia Road No.333, Pudong New Area, Shanghai
BD Cooperation Email: BD@novopathway.com Tel: 021-5838 0618-501
Join Us Email: HR@novopathway.com Tel: 021-5838 0356

Beijing Sun-Novo Pharmaceutical Research
Building No.7, West Shuangying Road No.79 , Changping Area, Beijing
Website: http://www.sun-novo.com




