- About Us
- One Stop Service
- Platform
In-Vitro
Molecular Assays
Cell-Based Functional Assays
In-Vivo
Pharmacology
Cancer PharmacologyInflammation Pharmacology - Join Us
- Contact Us
- Drug Discovery
- Molecular Assays
- Cell-Based Functional Assays
- Immune Functional Assays
- Tumor Pharmacology Platform
- Inflammation Pharmacology Platform
- In-Vitro ADME/DMPK
- In-Vitro Toxicology
- Pharmacology
- Cancer Pharmacology
- Inflammation Pharmacology
- In-Vivo ADME/DMPK
- In-Vivo Toxicology
- In-Vivo Pathology
- Clinical Laboratory
In-Vivo Pathology
Background
Pathology is the etiology, pathogenesis and local tissue structure changes of the disease progression. After pathological examination to reveal the occurrence and development of the disease, clinically used to check whether the local inflammation infection, diseased tumor, or proliferative disease, can also judge the nature of the tumor.
Pathological section is a kind of pathological specimen, part of the diseased tissue or organ after various pre-treatment, fix and harden, cut into thin slices on the microtome, stained with various colors and examined under a microscope to observe pathological changes, make pathological diagnosis, and provide help for clinical diagnosis and treatment.
Novopathway can provide customers with a variety of pathology testing services, including H&E Staining, Immunohistochemical Staining, Immunofluorescent Staining and special staining services. By understanding our customers' specific requirements, we developed tested SOP to optimize immunohistochemistry experimental conditions in several aspects, including tissue fixation methods, antigen activation conditions, antibody titer selection, incubation time, and washing conditions.
Preparation of tissue sections:
Customers can provide fresh tissues, which is fixed and embedded in paraffin by us. Frozen or paraffin-embedded tissue or cell samples may also be provided for analysis.
Selection of antibody:
Customers can provide the primary antibody required for detection, or we can be responsible for screening antibodies from existing antibodies. The secondary antibodies for the assay were provided by us.
Pathological staining services
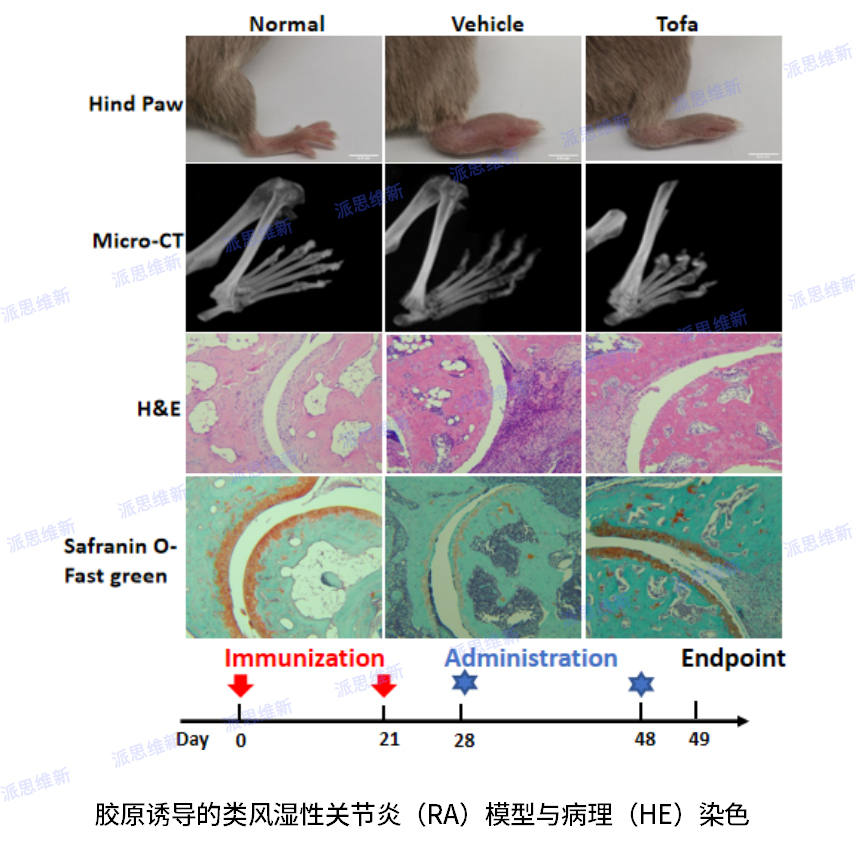
Collagen-induced rheumatoid arthritis model with Bone tissue staining
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic, systemic autoimmune disease with invasive, symmetric polyarthritis as the main clinical manifestation. The main pathological damage is synovial inflammation of the joint, cell infiltration, synovial pntomy, when cartilage and bone are involved, it can lead to the destruction of joint structure, deformity and dysfunction, causing varying degrees of disability. The genetic background and immunopathological changes of collagen-induced arthritis models are similar to RA diseases, and not only have acute lesions, but also have certain chronic lesion characteristics. The clinical manifestations are multiple peripheral arthritis, and the pathological changes are mainly proliferative synovitis, followed by the destruction of articular cartilage until the destruction of bone, and the infiltration of monocytes and persistent presence in the synovium.
Safranin-O Fast Green staining makes basophilic cartilage combine with the basic dye crosa to show red, and eosinophilic bone and acid dye solid green combine to form blue, which contrasts sharply with red cartilage, thereby distinguishing cartilage tissue and bone tissue.
Hematoxylin-Eosin staining, referred to as HE staining, is one of the commonly used staining methods in paraffin sectioning technology. Hematoxysperm staining solution mainly makes the chromatin in the nucleus and the ribosome in the cytoplasm violet-blue; Einson mainly makes cytoplasm, interstitium, and various fibers appear red to varying degrees.
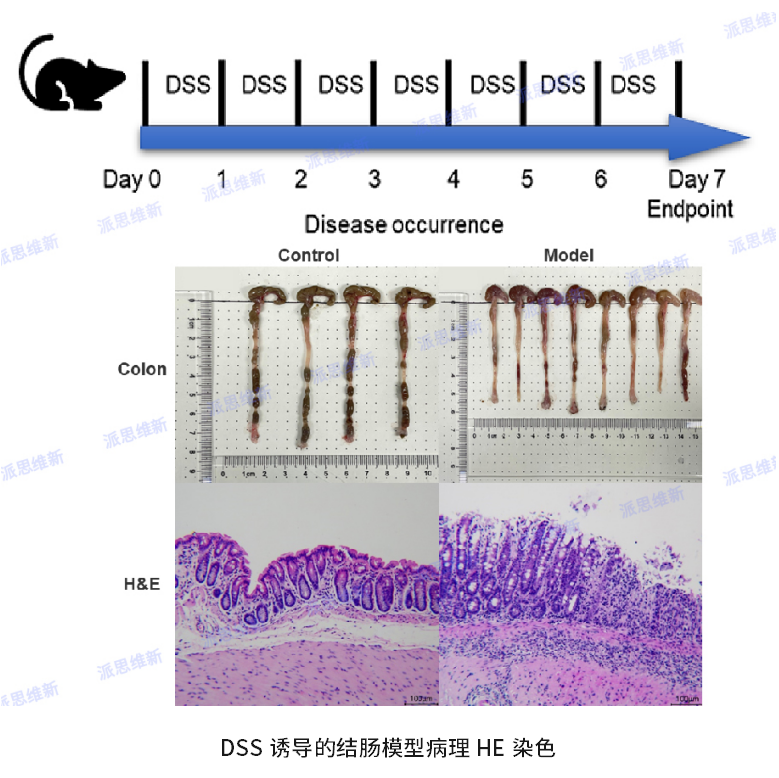
DSS-induced UC colon model,H&E Staining
Colorectal cancer is the third leading cause of death in cancer patients worldwide. It’s a spontaneous, chronic inflammatory lesion of the colonic mucosa. Studies have found that the two most common chronic inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) in humans are Ulcerative Colitis (UC) and Chron's disease (CD). They are all associated with colorectal cancer. Since Japanese scholars first used dextran sulfate (DSS) to establish a murine UC model in 1985, a large number of animal models have been applied to the study of UC, and DSS-induced colitis model is one of the most widely used UC models.
By dissolving DSS in drinking water to induce acute ulcerative enteritis or chronic colitis, disrupting mouse intestinal epithelial cells, releasing non-specific immune cytokines, and ultimately leading to the destruction of the integrity of the mucosal barrier, animals exhibit significant weight loss, loose stools, blood in the stool and granulocyte infiltration, and its clinical symptoms and pathological features are very similar to human ulcerative colitis.
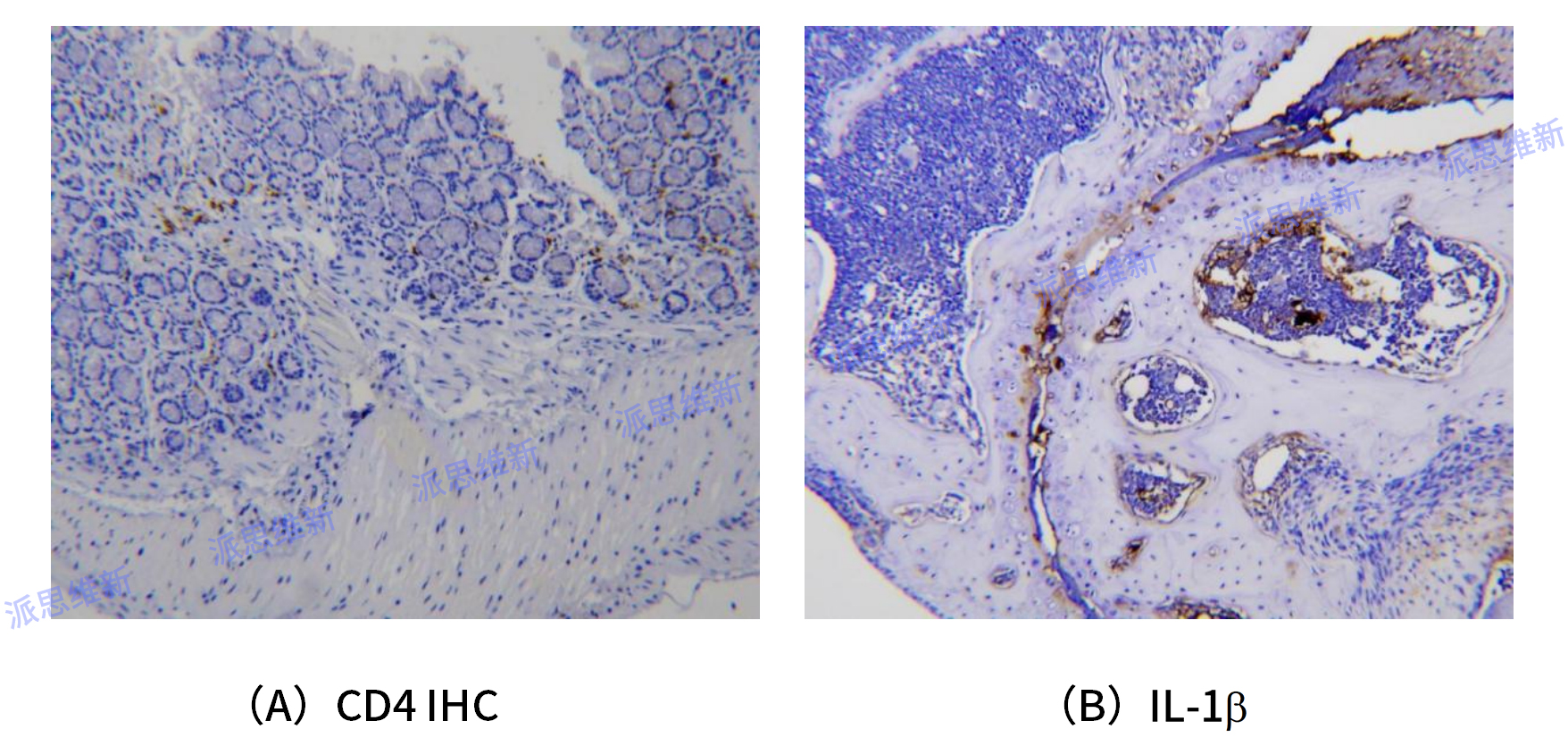
Immunohistochemical Saining
Immunohistochemistry (IHC): Based on the principle of antigen-antibody specific binding, the color developer (luciferin, enzyme, metal ion, isotope) of the labeled antibody is used to determine the antigens (such as peptides and proteins) in tissue cells through chemical reactions, and its localization, qualitative and quantitative research.
Immunohistochemistry technology is applied to the field of biological detection (including the diagnosis of abnormal cells, the distribution of biomarkers, the detection of differential expression of proteins in different parts of biological tissues, etc.). With the help of microscopy imaging and magnification, various antigenic substances (such as proteins, peptides, enzymes, hormones, pathogens, receptors, etc.) can be detected at the cellular and subcellular levels.
Fiber Staining
Masson Trichrome Staining, also known as Masson trichrome staining, is the most classical method in the staining of connective tissues (including collagen fibers, reticular fibers, and elastic fibers), and is an authoritative and classic technical method for collagen fiber staining. Masson staining was used to distinguish between collagen fibers and muscle fibers by showing red muscle fibers and green or blue collagen fibers.

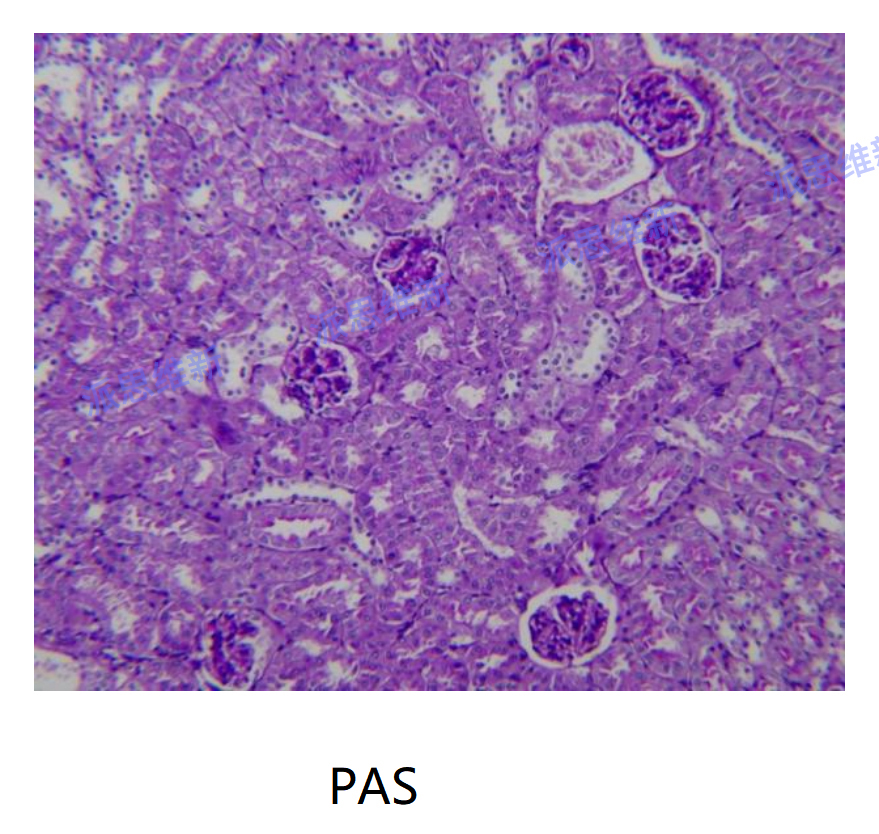
Glycogen staining
Periodic Acid Schiff Staining (PAS) is referred to as glycogen staining. In histology, it is mainly used to detect glycogen and other polysaccharide substances in tissues. After PAS staining, the glycogen or polysaccharide substances (such as glycoprotein, mucopolysaccharide, glycolipid, mucin, etc.) in the cytoplasm of cells will appear purple red when combined with colorless fuchsin in Schiff reagent.

Shanghai Novopathway Biotechnology
Building No.5, East Huaxia Road No.333, Pudong New Area, Shanghai
BD Cooperation Email: BD@novopathway.com Tel: 021-5838 0618-501
Join Us Email: HR@novopathway.com Tel: 021-5838 0356

Beijing Sun-Novo Pharmaceutical Research
Building No.7, West Shuangying Road No.79 , Changping Area, Beijing
Website: http://www.sun-novo.com




